- The AI Timeline
- Posts
- Learning to Discover at Test Time
Learning to Discover at Test Time
plus more on Memorization Dynamics in Knowledge Distillation and Efficient Agents
Jan 20th ~ Jan 27th
#92 Latest AI Research Explained Simply
🗞️ Industry News in 1 Line
♥ 11k Moltbot is THE personal AI assistant everyone imagined AI to be. Previously known as Clawdbot, it is an open source AI assistant that can connect messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Telegram, and Slack to a private gateway running on your own hardware. It can run seamlessly on Linux and Windows (via WSL2), and it even integrates with iMessage (requires macOS hardware) and automate everything for you. Just be aware of security when setting it up!
♥ 44k Claude has released a beta integration that adds AI reasoning directly into your spreadsheets to analyze complex formulas and multi-tab dependencies. The tool allows you to debug errors, update assumptions, and build models while preserving your original structure, all accessible via a simple keyboard shortcut. Unlike standard chat interfaces, it provides transparent explanations with cell-level citations, ensuring you can verify the logic behind every calculation.
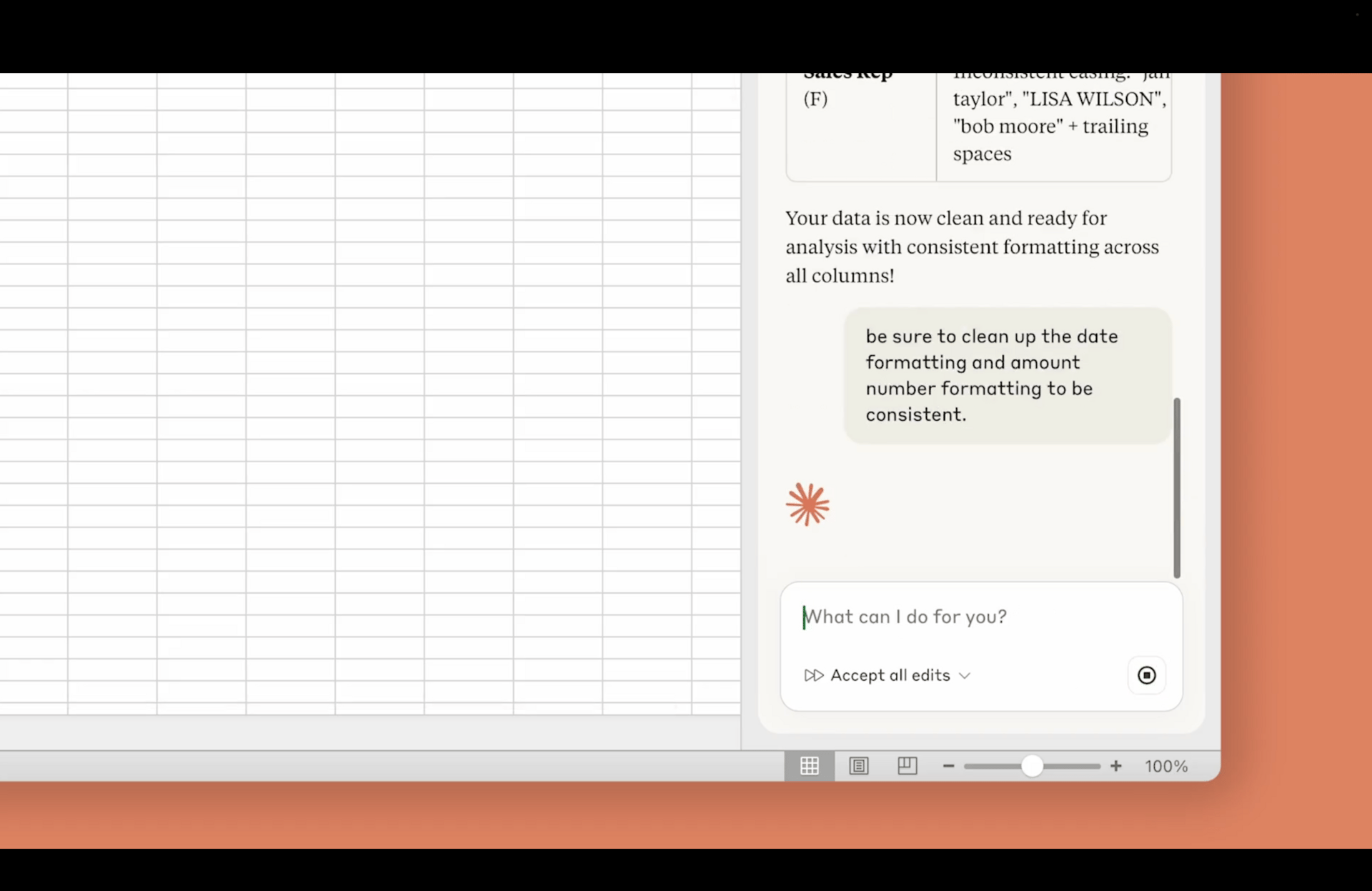
♥ 6.1k Qwen has open-sourced the Qwen3-TTS family, which is a suite of high-performance speech generation models (1.7B and 0.6B) that deliver state-of-the-art voice cloning and design across 10 languages. It is built on a novel non-DiT architecture with Dual-Track modeling, the tool enables ultra-low latency streaming (outputting audio after a single character input) and allows for precise control over emotion, tone, and prosody via natural language instructions. Try it on Hugging Face or via the Alibaba Cloud API.
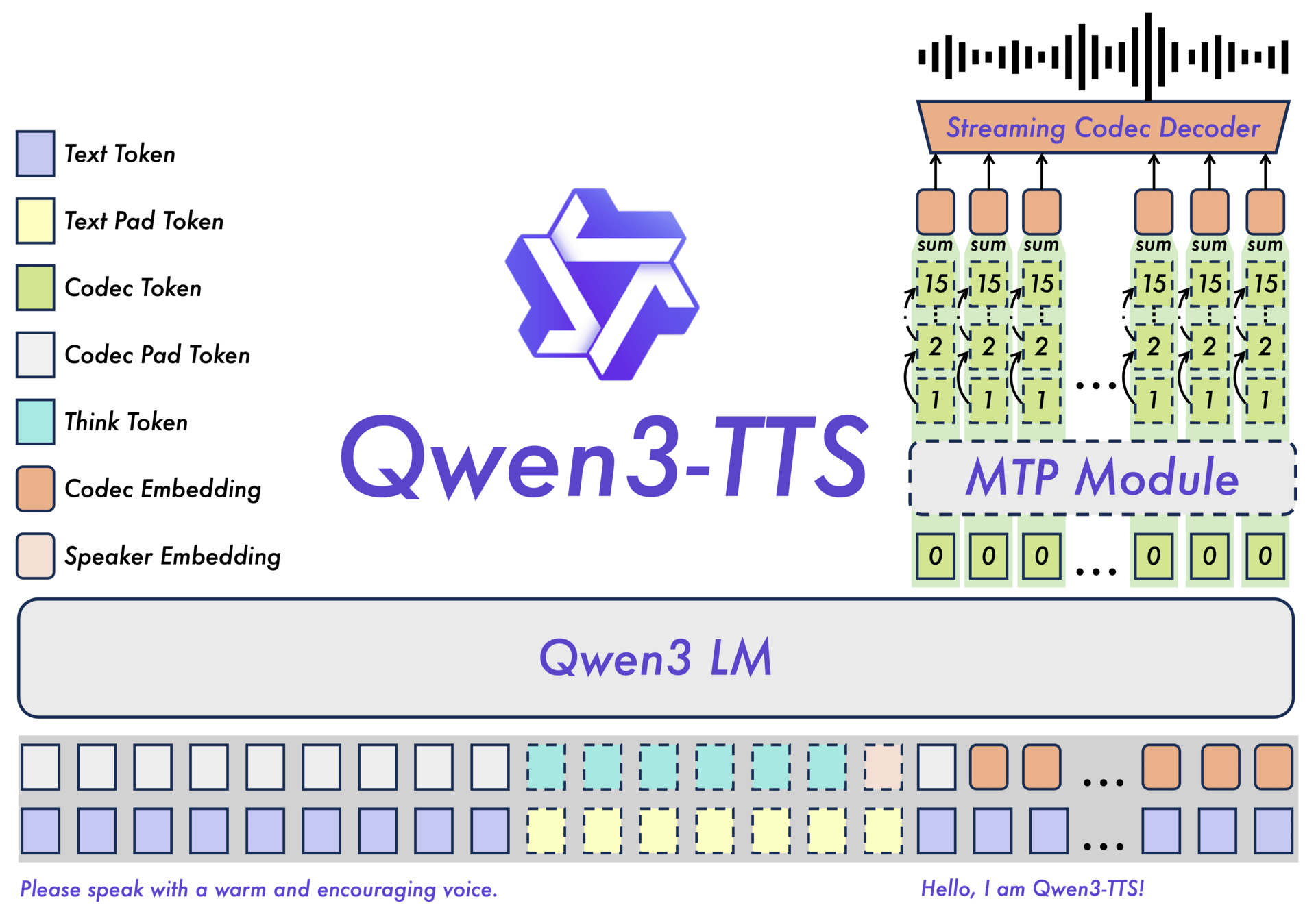
♥ 4.4k Excalidraw has added a new "smarter, faster, stronger" text-to-diagram feature that uses a streaming chat interface for real-time visual generation. This update is accessible now within the free version of the tool (with some usage limits) and remains open-source on GitHub, though users may need to refresh their browser cache or use incognito mode to ensure they aren't loading the older build.
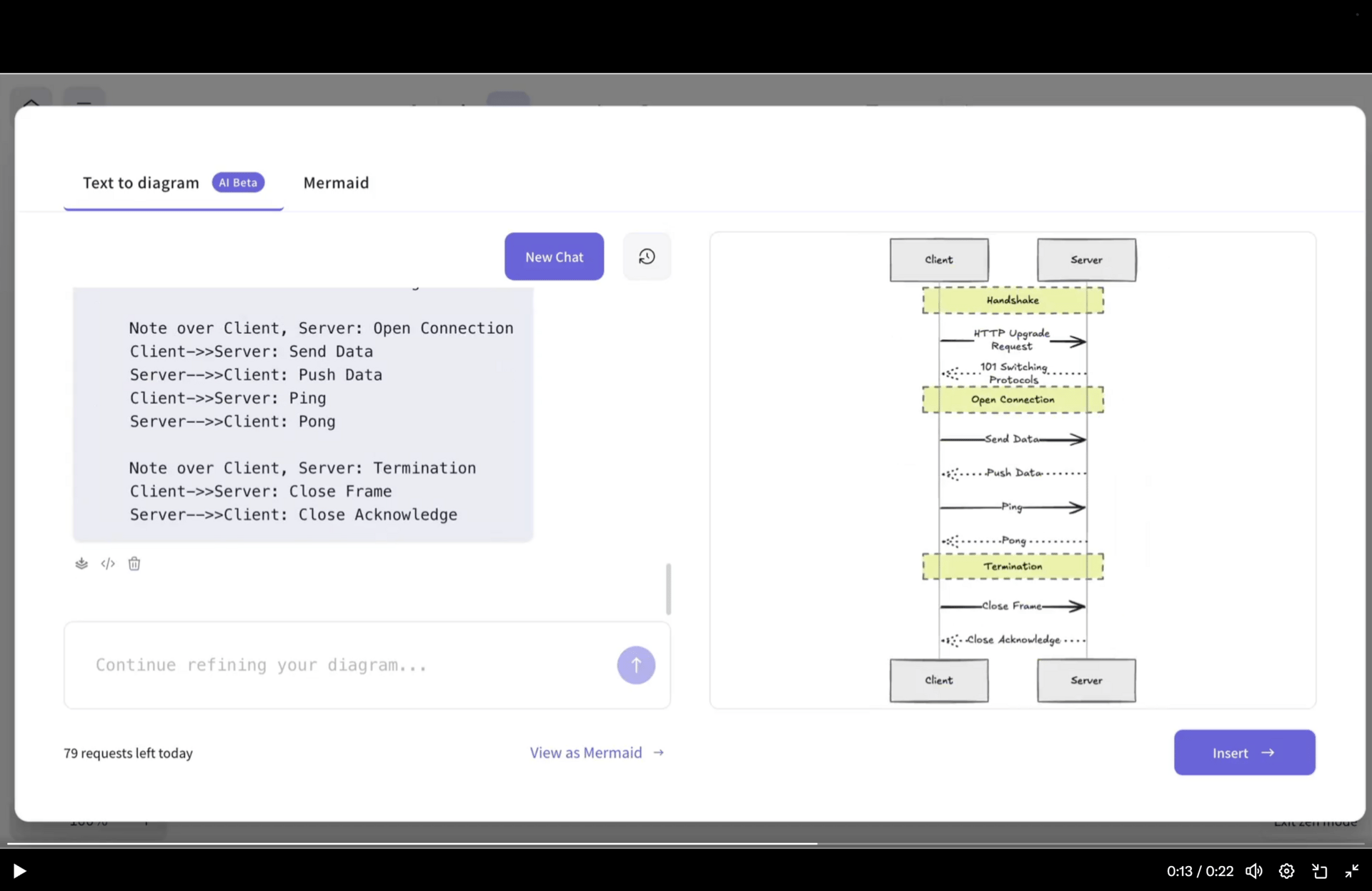
♥ 7.4k Moonshot AI has released Kimi K2.5, an open-source visual agentic model that achieves state-of-the-art performance on major benchmarks, including HLE (50.2%) and BrowseComp (74.9%). The model excels at converting multimodal inputs (like chats, images, and videos) into fully functional, aesthetic websites and features a beta "Agent Swarm" capability that allows up to 100 self-directed sub-agents to collaborate on complex tasks 4.5× faster than single-agent setups. Try it now or download from Hugging Face.
Learn LLMs Intuitively - Intuitive AI Academy
Want to learn about LLMs, but never have a good place to start?
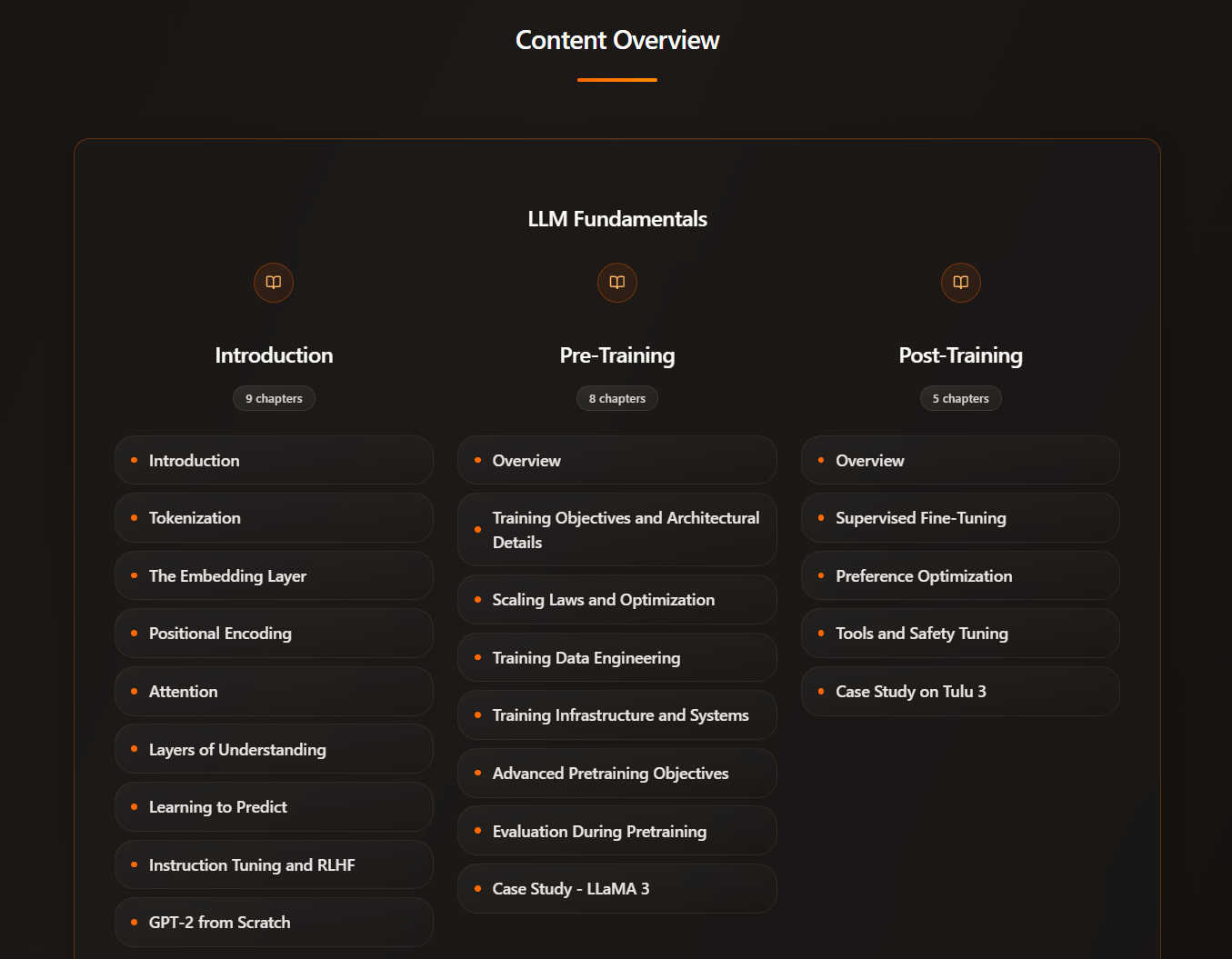
Intuitive AI Academy has the perfect starting point for you! We focus on building your intuition to understand LLMs, from transformer components, to post-training logic. All in one place.
We have just added a brand new chapter, an in-depth walkthrough of the current LoRA research landscape. Coming up next is MoE.
We currently have a New Year New Me launch offer, where you would get 50% off yearly plan FOREVER for our early users. Use code: 2026
Memorization Dynamics in Knowledge Distillation for Language Models
Borkar et al. [Meta Superintelligence Labs, Meta Central Applied Science, FAIR at Meta, Northeastern University, Carnegie Mellon University]
♥ 502 Knowledge Distillation
Knowledge distillation is a process where a highly capable "teacher" AI helps train a smaller, more efficient "student" model. It allows us to capture the teacher's intelligence without the massive computational cost. However, large models are notorious for memorizing specific snippets of their training data, from phone numbers to unique sentences.
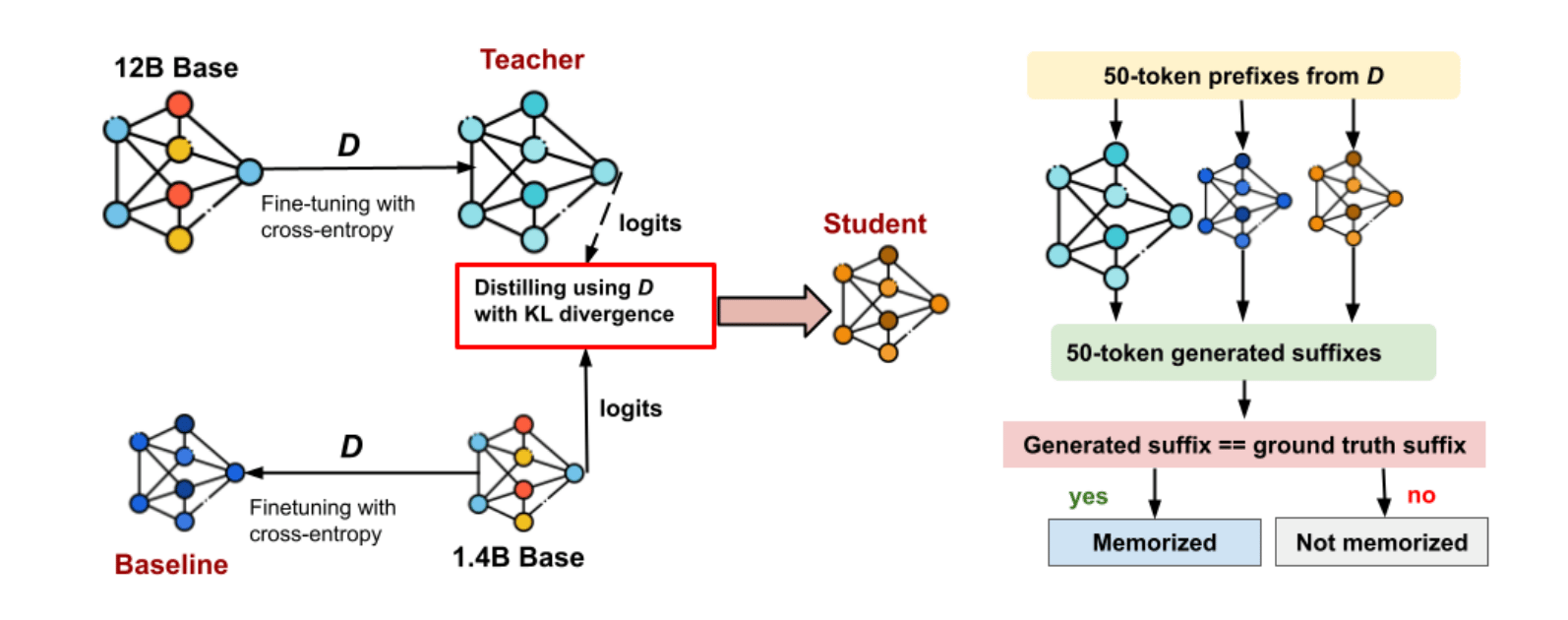
Experimental framework
The researchers of this paper want to know does the student simply parrot the teacher's memories, or can it learn to think like the teacher while forgetting the specific, sensitive data that was used for training?
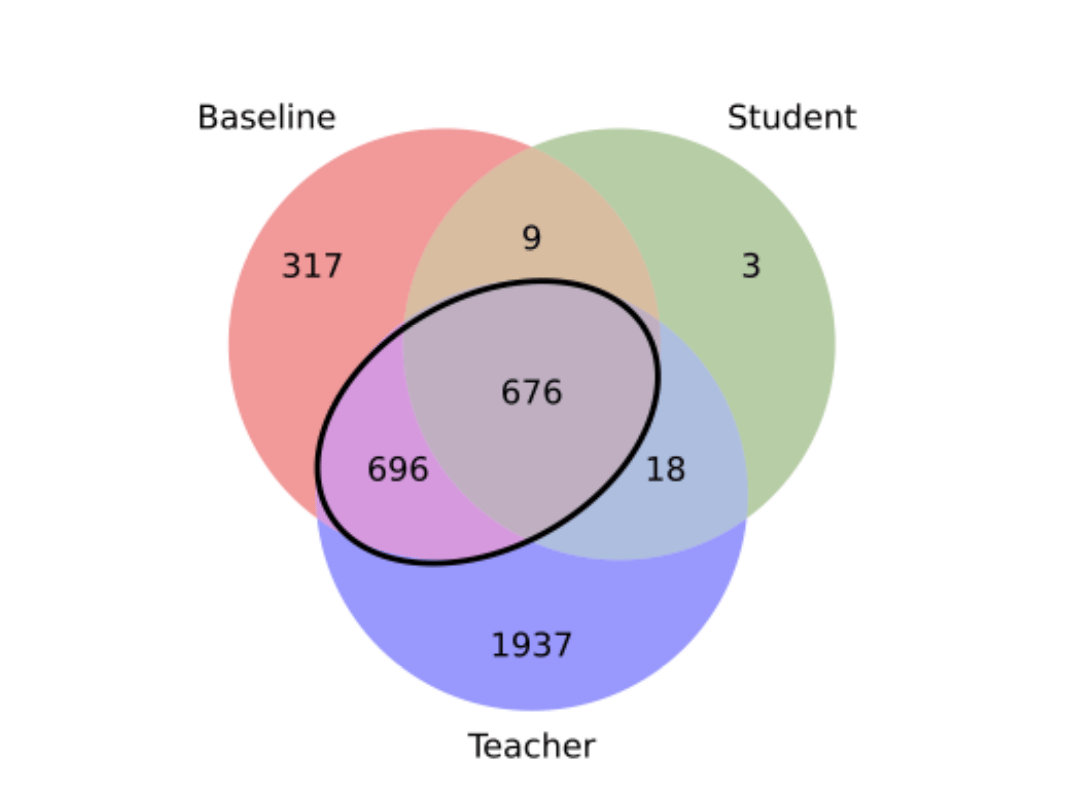
Overlap of memorized examples.
The study shows that when a student model learns from a teacher, it actually acts as a privacy filter. These distilled models ended up memorizing significantly less training data, cutting the rate of memorization by more than half compared to models trained the standard way. It turns out that the student primarily holds onto "easy" information that is simple to compress and understand, while successfully rejecting the complex, specific examples that the teacher had memorized.
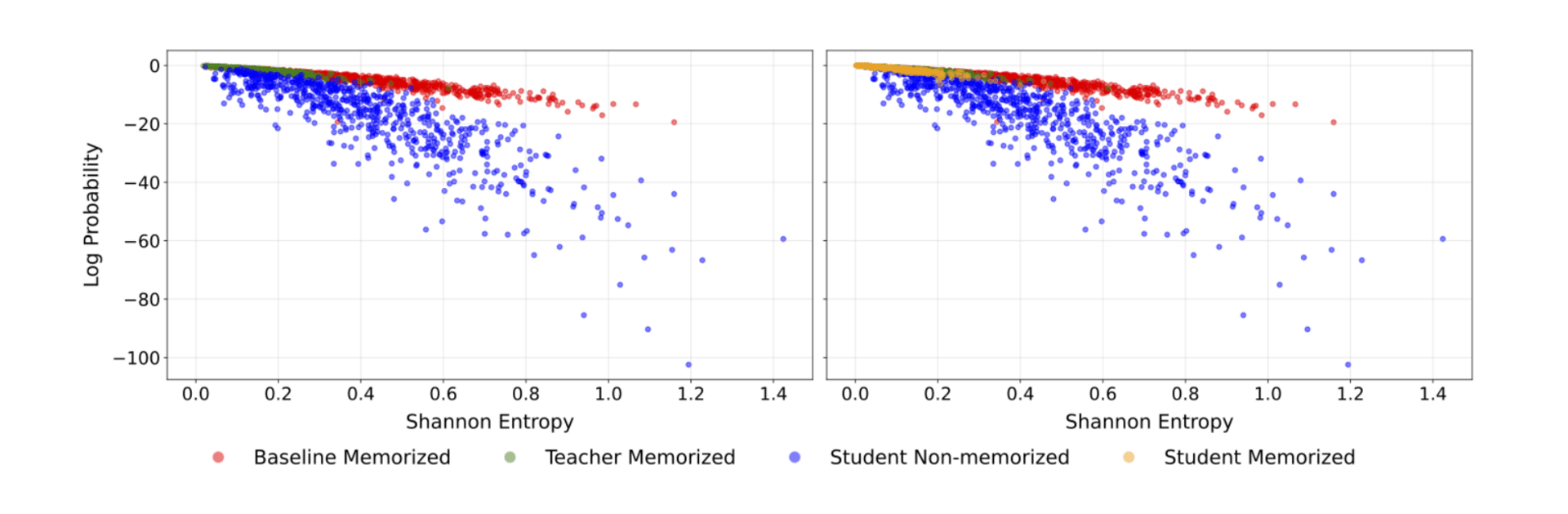
Shannon Entropy vs. Log-Probability Analysis.
By allowing the student to mimic the teacher’s uncertainty rather than forcing it to memorize hard answers, the distillation process naturally prevents the model from overfitting to specific training examples. The student effectively learns the general skills without retaining the exact data used to teach them.
Learning to Discover at Test Time
Yuksekgonul et al. [Stanford University, NVIDIA, Astera Institute, UC San Diego, Together AI]
♥ 680 LLM bycloud’s pick
Until now, most AI models have functioned like the student who stops learning once the test begins; they are "frozen" and can only search for answers based on past training. To succeed, they need to learn and adapt in the moment, internalizing new concepts from their own failed attempts.
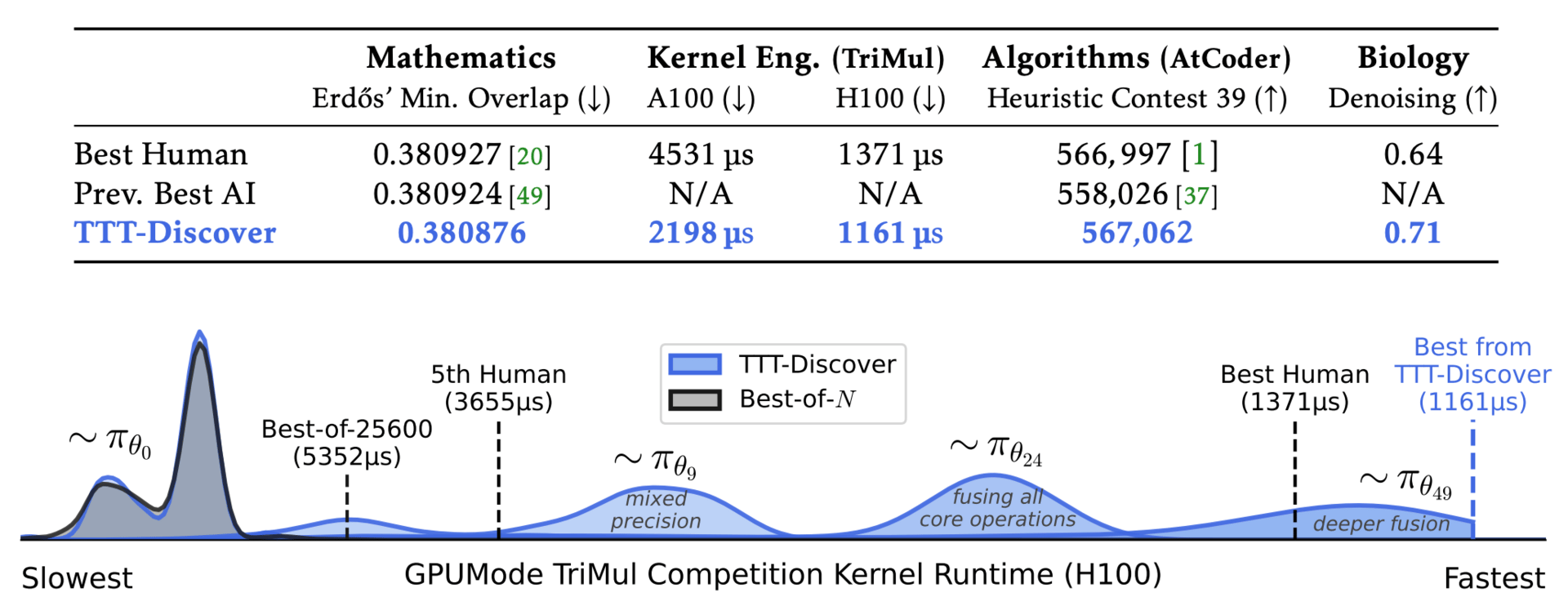
TTT-Discover continues to train an LLM on a single problem at test time.
The researchers for this paper have developed a method called "Test-Time Training to Discover". Instead of trying to be good at everything on average, this approach allows the AI to become a hyper-specialist on a single problem. By using reinforcement learning during the test phase, the model treats its own search attempts as new training data, ignoring safe, average answers to hunt for the single, exceptional "eureka" moment.
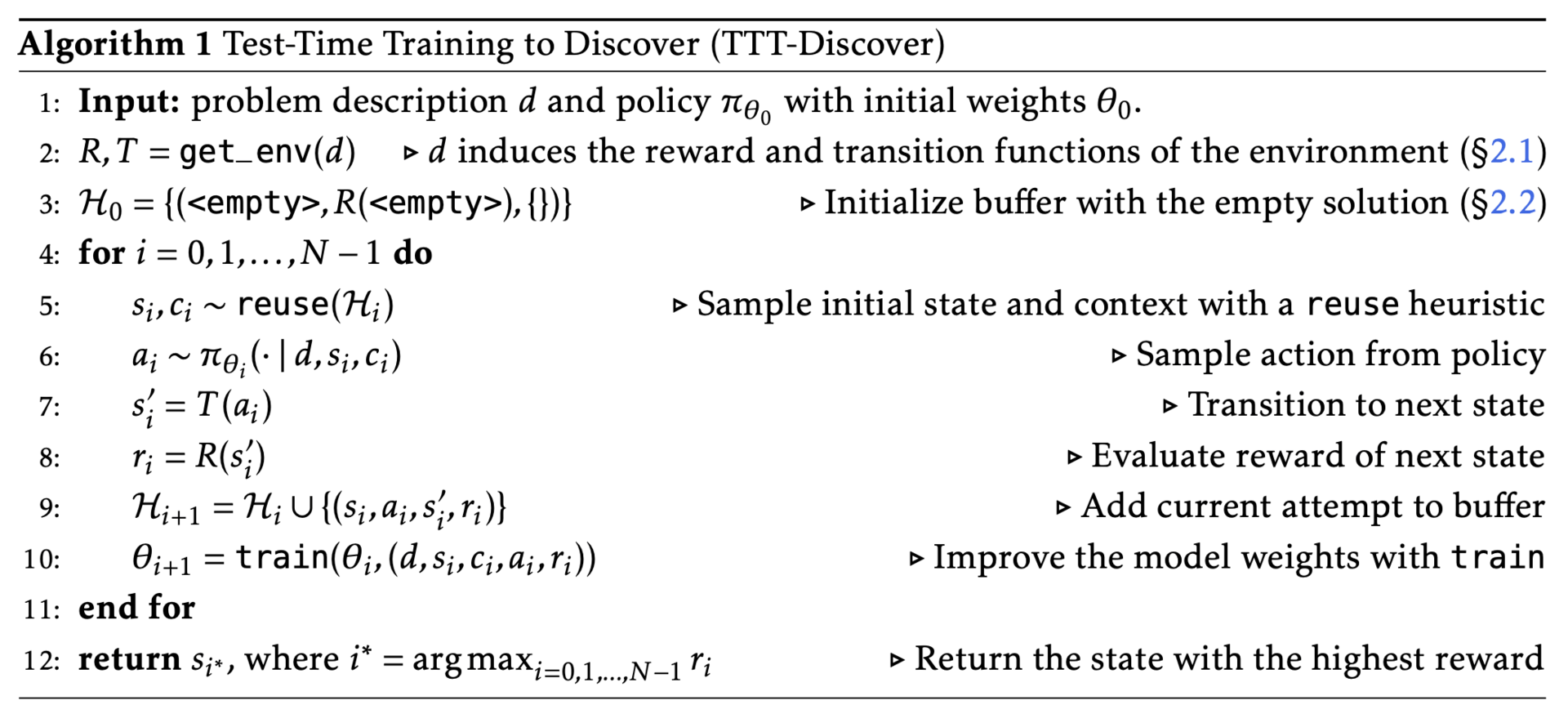
In mathematics, the system improved upon the bounds of a problem posed by Erdős in 1955, discovering a complex, asymmetric solution that had eluded both human mathematicians and previous AI systems.
In computer engineering, it wrote code for GPU chips that ran significantly faster than kernels hand-optimized by human experts. It achieved these state-of-the-art results using an open-source model, outperforming larger, proprietary models simply by having the freedom to learn while it worked.
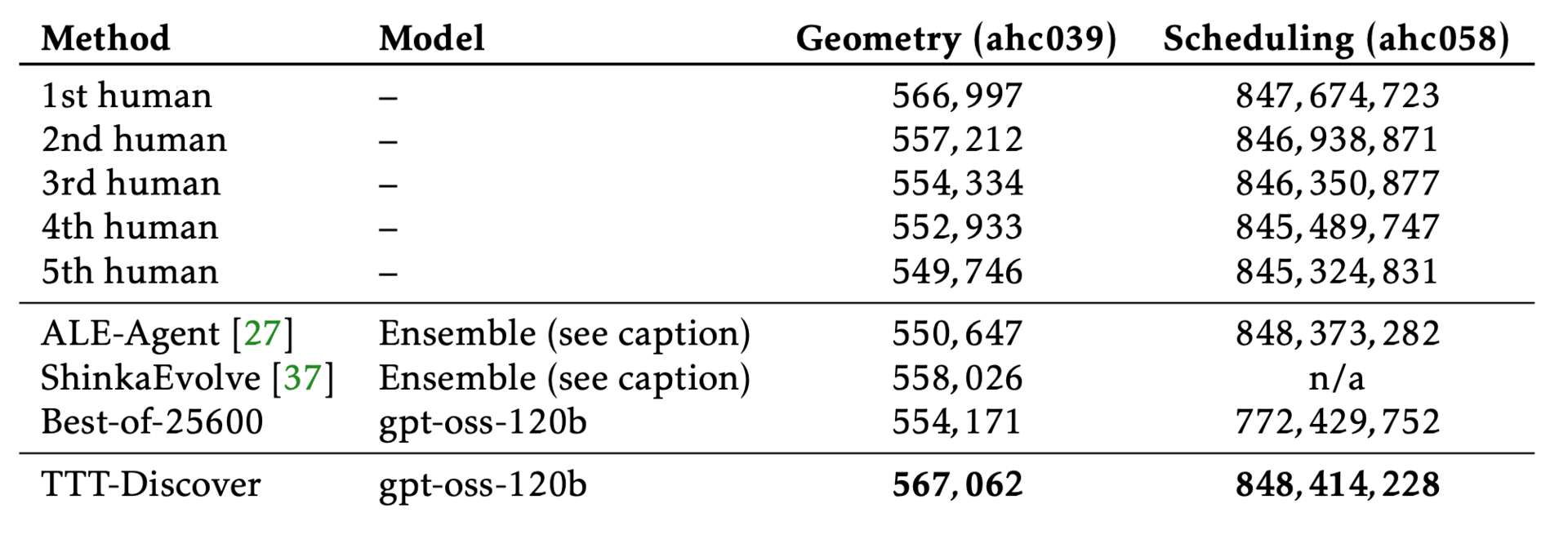
Results in two AtCoder Heuristic Competitions.
By shifting the focus from massive, static training to dynamic, problem-specific adaptation, this research has opened the door to solving highly specific challenges in biology, engineering, and mathematics that currently seem out of reach.
Toward Efficient Agents: Memory, Tool learning, and Planning
Yang et al. [Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, Fudan University, University of Science and Technology of China, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Chinese Academy of Sciences, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (Shenzhen), Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Wuhan University, Tsinghua University]
♥ 96 LLM Agents Survey
AI models can generate text, but we need "agents" capable of actively interacting with the world to execute complex workflows. However, this autonomy comes with a heavy price. Unlike a standard chatbot that answers a question and moves on, an agent operates in a recursive loop (planning, acting, remembering, and observing).
This creates a compounding accumulation of information, where the output of one step becomes the costly input for the next. This paper aims to solve the problem of "context window saturation" to ensure that AI systems remain sustainable, responsive, and accessible to everyone rather than becoming too computationally expensive to run.
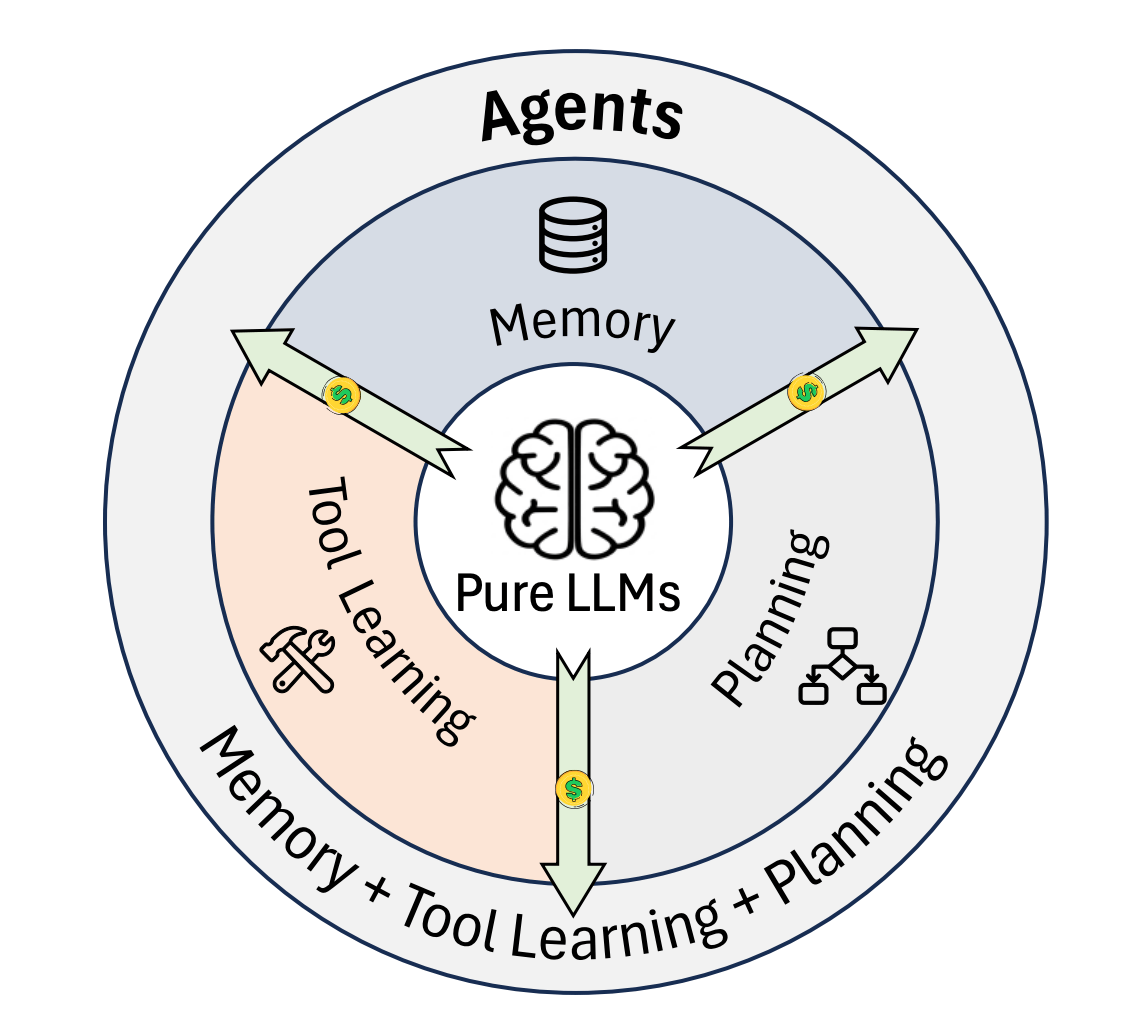
From LLMs to agents: standalone reasoning to trajectory-level reasoning with memory, planning, and tool learning, while introducing additional cost sources.
This survey suggests that creating an "efficient agent" does not simply mean building a smaller model; it requires optimizing the entire system to maximize success while minimizing resource consumption. The researchers found that efficiency gains come from rethinking three specific areas: memory, tool usage, and planning.
In terms of memory, the field is moving away from forcing an agent to re-read every past interaction. Instead, new techniques allow agents to compress history into summaries or "latent" states, essentially giving the AI a working memory that retains the gist of a conversation without the computational weight of the raw text.
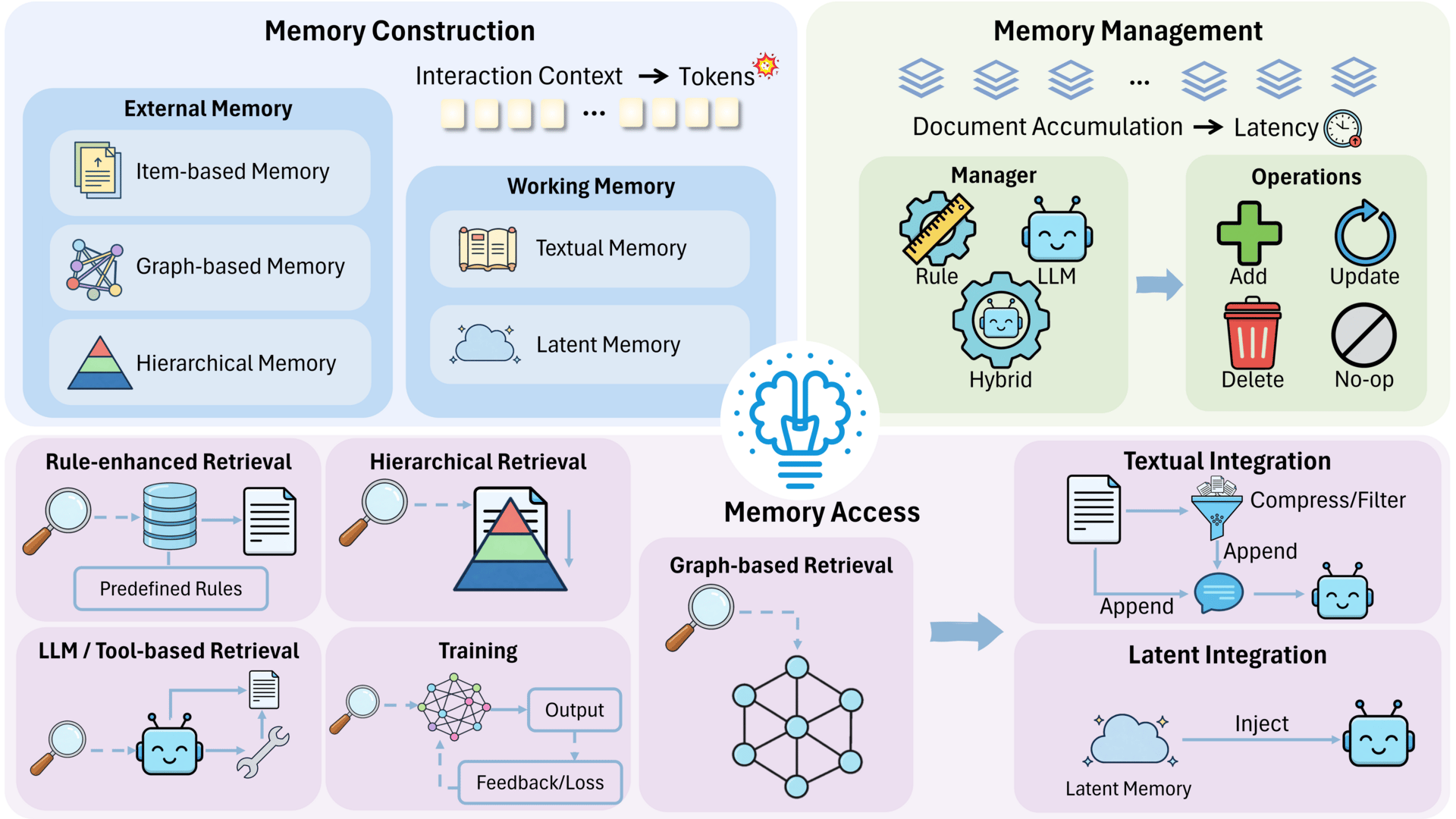
Efficient memory overview.
When it comes to using external tools, we should focus on optimizing how the agent interacts with its environment. Rather than testing tools sequentially or randomly, efficient agents are now using sophisticated retrieval systems to identify the correct tool instantly. Advanced agents can also perform parallel execution, where agents can run multiple tasks simultaneously rather than waiting for one to finish before starting another, drastically reducing the latency between a thought and an action.
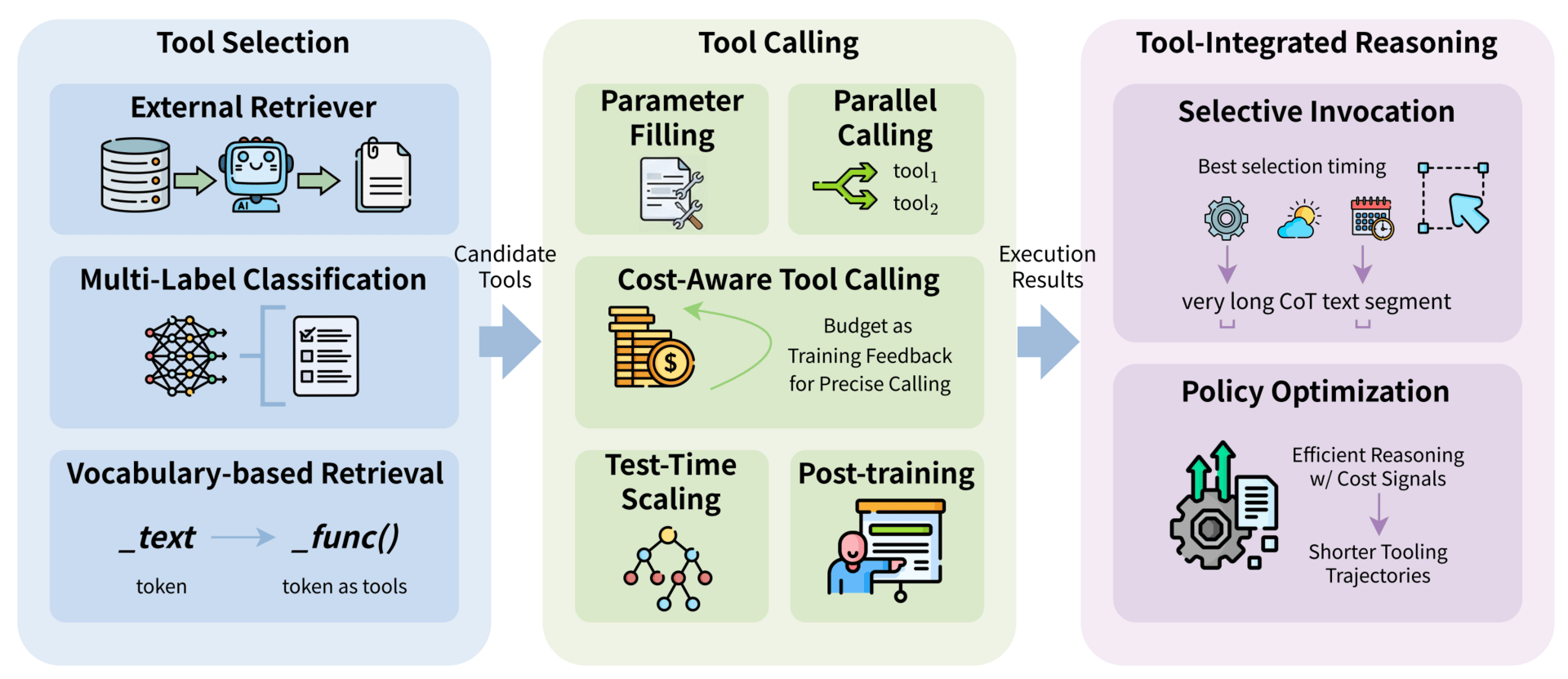
Efficient tool learning comprises three stages
The researchers propose reimagining how agents plan their next moves by treating "thinking" as a limited resource. Instead of allowing for unbounded reasoning, new methods introduce the concept of "budgeted deliberation."
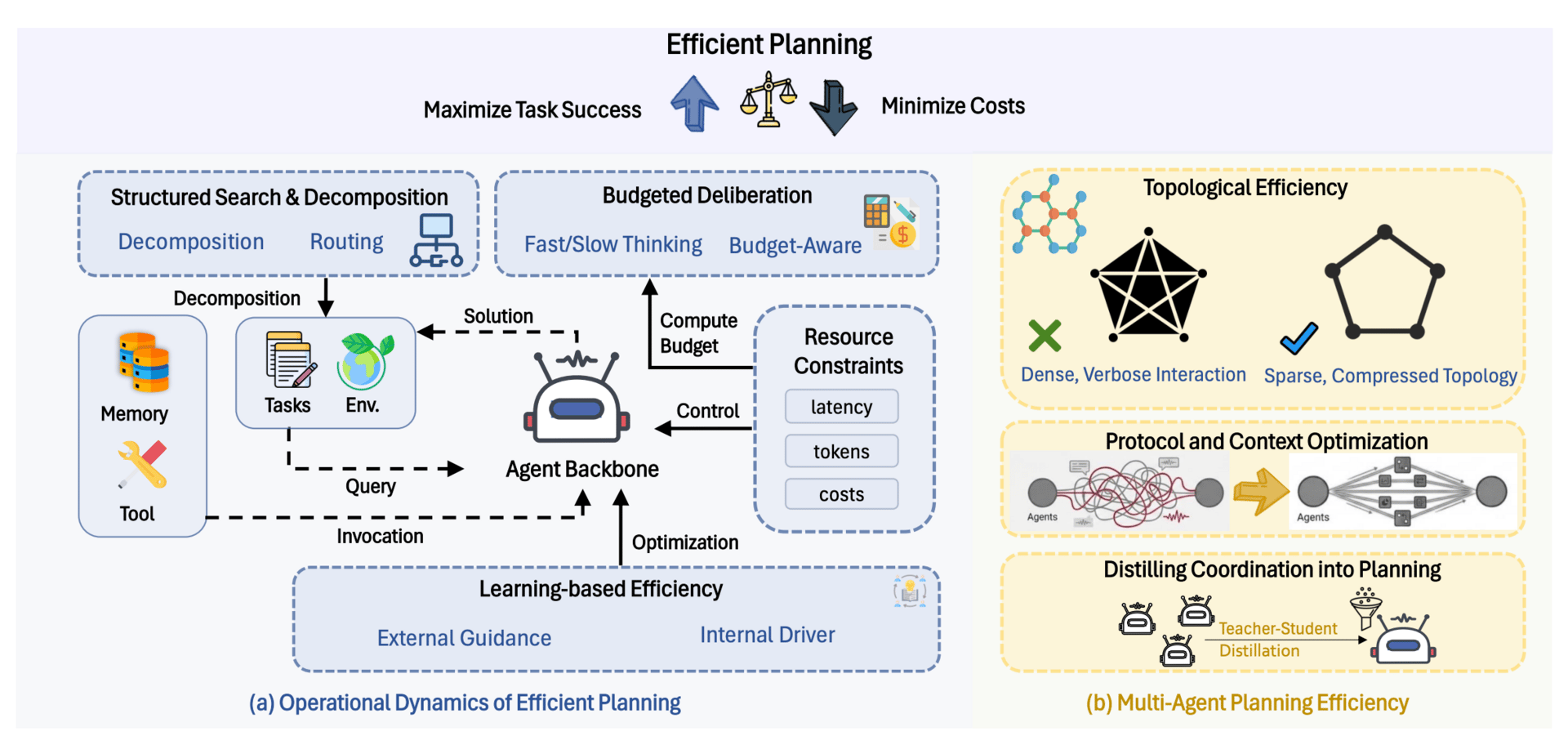
Overview of Efficient Planning.
By using reinforcement learning, systems are being trained to value brevity, effectively rewarding the agent not just for getting the correct answer, but for solving the problem with the fewest possible steps and the least amount of computational effort.
Reply