- The AI Timeline
- Posts
- Using Diffusion To Interpret LLMs?! Generative Latent Prior
Using Diffusion To Interpret LLMs?! Generative Latent Prior
plus more on Evolving Agents via Recursive Skill-Augmented RL and Low Hanging Fruits in Vision Transformers
Feb 9th ~ Feb 16th
#95 Latest AI Research Explained Simply
🗞️ Industry News in 1 Line
♥ 5.7k Google DeepMind has upgraded its Gemini 3 Deep Think reasoning mode to tackle complex scientific and engineering challenges. This new mode is setting new performance records on frontier benchmarks like ARC-AGI-2. You can access it via Google AI Ultra subscription and is available to researchers via a Vertex AI Early Access Program.

♥ 3.1k Zhipu AI’s GLM-5 has demonstrated the ability to manage over 700 tool calls and 800 context handoffs during continuous 24-hour operations. This advancement allows AI agents to handle highly complex, multi-step workflows, such as autonomously reverse-engineering software code from visual video demonstrations. Currently #1 open source model, and beating Gemini-3-Pro-high.

♥ 8.9k MiniMax has launched M2.5, an open-source model that delivers state-of-the-art performance in coding, search, and agentic tool-calling, including a top-tier 80.2% score on SWE-Bench. This model is optimized for productivity and it is 37% faster and can be used as a drop-in replacement for Claude Code via its coding plan.

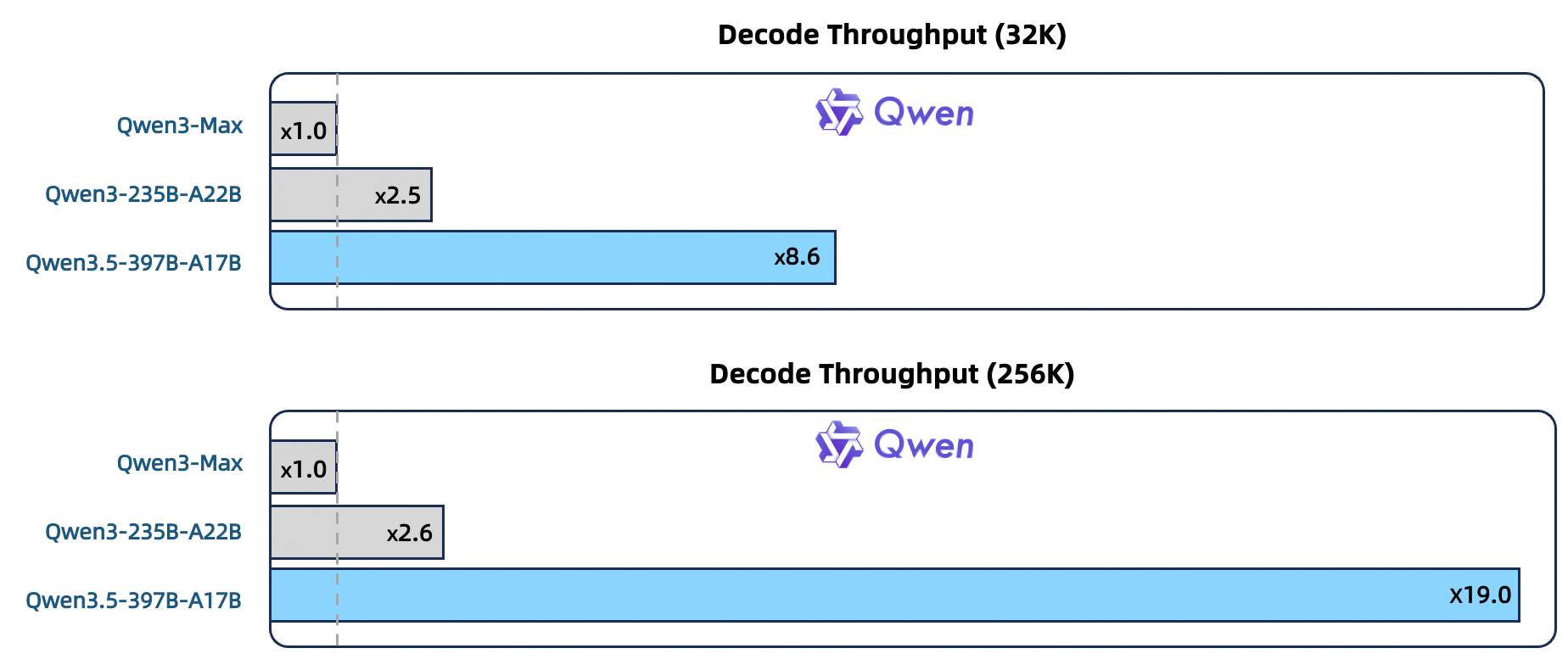
♥ 4.2k Alibaba has published Qwen3.5-397B-A17B, its first open-weight, native multimodal model featuring a sparse Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture that is optimized for real-world agents. It is licensed under Apache 2.0 and it supports over 200 languages and delivers up to 19 times the decoding throughput of its predecessor through advanced reinforcement learning environment scaling.
Learn LLMs Intuitively - Intuitive AI Academy
Want to learn about LLMs, but never have a good place to start?
My latest project: Intuitive AI Academy has the perfect starting point for you! We focus on building your intuition to understand LLMs, from transformer components, to post-training logic. All in one place.
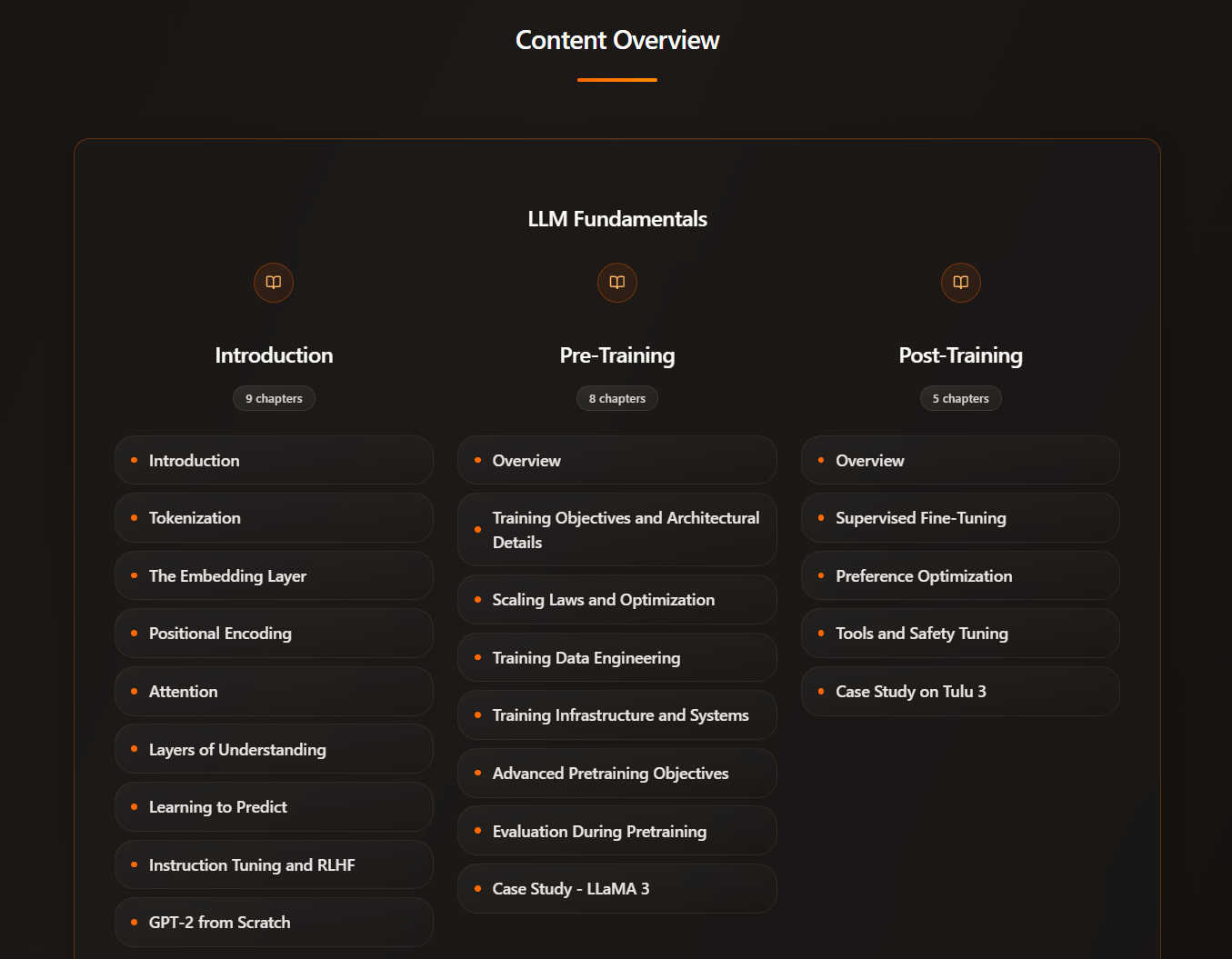
content overview (a total of 100k words explainer so far!)
ViT-5: Vision Transformers for The Mid-2020s
Wang et al. [Johns Hopkins University, UC Santa Cruz]
♥ 1k ViT
LLMs are sprinting ahead with rapid architectural refinements, but Vision Transformers (ViTs) have remained largely stagnant since their debut in 2020. Vision models struggle with stability issues and a limited ability to handle complex spatial reasoning.

ViT architecture
The research team developed ViT-5 by systematically testing five years of AI advancements to see which ones actually improve a model's "eyesight." They discovered that simply copying language model tricks doesn't always work; for instance, a popular method for filtering information in text models actually caused "over-gating" in vision, making the internal representations too sparse to be useful.

Instead, they found success by combining a more efficient normalization method with a clever dual-positioning system. This allows the model to understand where every pixel is relative to its neighbors while still maintaining a "big picture" sense of the entire image.

To further refine performance, the researchers introduced "register tokens," which act like digital scratchpads to clean up visual artifacts and help the model focus on what is semantically important. They also implemented a technique called QK-normalization, which smoothed out the training process and eliminated the frustrating "error spikes" that often crash large-scale AI projects.
The final model can handles images of varying sizes with ease and consistently outperforms previous standards in identifying objects and generating new images.
SkillRL: Evolving Agents via Recursive Skill-Augmented Reinforcement Learning
Xia et al. [UNC-Chapel Hill, University of Chicago, University of California San Diego, NEC Labs America, University of California Berkeley, University of California Santa Cruz]
♥ 455 Skill bycloud’s pick
Even the most advanced models often treat every new task as a blank slate. Researchers have long tried to give these agents a memory, but simply feeding them long, messy logs of past actions often results in "noisy" confusion that slows the system down.
The team behind SKILLRL realized that for AI to truly evolve, it shouldn't just record what happened; it needs to distill those experiences into compact, actionable skills. This team developed a framework that transforms raw, verbose interaction data into a structured "SkillBank."

Instead of saving every redundant step of a task, the system uses a teacher model to extract the core logic behind a success and the critical lessons from a failure. These insights are organized into a hierarchy: general principles for broad strategy and specialized tactics for specific tasks.
To make this work, the researchers introduced a recursive evolution process. As the agent practices using reinforcement learning, it doesn't just improve its own performance; it simultaneously updates its library.

When the agent hits a new type of roadblock, the system analyzes the failure, writes a new "skill" to handle it, and adds it to the collection. This co-evolution creates a virtuous cycle where the agent becomes more efficient and avoids "context bloat," using ten to twenty times less data than raw logs.
The results are striking, showing that smaller, open-source models can actually outperform massive, closed-source giants like GPT-4o by using this structured expertise.

Performance on ALFWorld and WebShop.
Learning a Generative Meta-Model of LLM Activations
Luo et al. [UC Berkeley, Transluce]
♥ 353 LLM Activations
Current tools for analyzing LLMs rely on rigid mathematical guesses that don't quite capture the messy, organic complexity of an AI’s inner workings. When we try to "steer" an AI toward a specific persona or sentiment, the intervention often corrupts the model’s internal logic, causing it to descend into repetitive or nonsensical babble.

To achieve this, the team developed a "meta-model" called a Generative Latent Prior, or GLP. Rather than forcing the data into simple boxes, they trained a massive diffusion model on over a billion internal states of a functioning language model. This meta-model effectively learns the "natural habitat" of the AI's internal activations.
When a human intervention pushes the AI into an unnatural or "off-manifold" state, the GLP acts as a corrective guide. It "denoises" the internal signal, pulling it back onto a path that makes sense to the language model while preserving the intended change in behavior.

GLP generates activation samples near-indistinguishable from real activations
This approach follows reliable scaling laws, meaning that as they invested more computing power, the meta-model became significantly better at predicting and refining the AI’s internal states. They also found that the meta-model’s own internal units, which they call "meta-neurons," are exceptionally good at isolating specific, human-understandable concepts like geography or mathematics.

Reply